Identification of Rice Leaf Diseases using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks

Introduction
Rice, a staple food of more than half of the world's population, employs one billion people, and rice farms cover around 150 million hectares—more than any other crop. Rice production is arguably the most important economic activity on the planet. Ricepedia (2020)
In Nepal, the use of rice is indispensable in the deeds of every Nepali from the birth to death and it is predominant even in various festivals celbrated throughout the year.

In Nepal, rice is cultivated, from 60m above sea level in the Terai to Chumchaur in Jumla(highes point), at an altitude of 3050m. Rice is cultivated in 47% of the total cultivable land in Nepal and provides more than 50% of the total calories requirements of Nepalese people. Not only is rice a key source of food, it is also a major employer and source of income for the people of Nepal. In Nepal, increased rice production is closely related not just with the national economic health but also with less hunger, better nutrition, lower levels of poverty and a better quality of life. Basnet (2021) Basnet (2021)

In Nepal, increased rice production is closely related not just with the national economic health but also with less hunger, better nutrition, lower levels of poverty and a better quality of life.
Various rice diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, Nematode can bring significant yield losses in the production and quality of rice grain. For example: Rice blast is responsible for approximately 30% of rice production losses globally the equivalent of feeding 60 million people Nalley (2016).
Leaf Blast, Brown Spot, Stem Rot, Yellow Dwarf etc are common rice diseases which damage various part of the plant and it is a big problem due to farmer’s lack of knowledge to identify different rice diseases. Early stage identification, precautions and advice in time will enable farmers to increase both quality and quantity of the production. But, the contemporary rice disease outbreak coping mechanism is slow and hectic. Whenever a rice disease outbreaks occurs, government send agriculture specialist to inspect those diseases. They use their naked eyes and experience to identify those disease, provide strategic decisions concerning the number and timing of fungicide applications.
Early stage identification, precautions and advice in time will enable farmers to increase both quality and quantity of the production.
But the number of such specialist is very low and monitoring of diseases over a large cultivation area is costly, cumbersome and time-consuming. Many of the time the sample may be taken to the laboratory for chemical tests which may take an awful lot of time. This deficiency in our contemporary disease outbreak coping mechanism shows an urgent need for the development and implementation of automatic rice disease detection mechanism.
This deficiency in our contemporary disease outbreak coping mechanism shows an urgent need for the development and implementation of automatic rice disease detection mechanism.
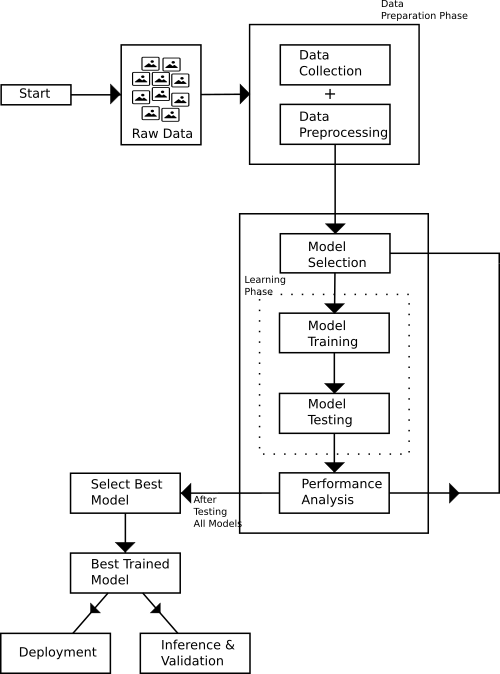
We propose an automated real-time rice disease identification and diagnosis system which performs the task of detecting rice diseases with minimal human intervention. This system based on deep learning technology automatically detects rice diseases from still image coming from a digital camera and provides necessary advice and strategic decisions to the farmer.
Team Members
Bibliography
B. M. S. Basnet. Hail the Humble Paddy. url: https://kathmandupost.com/opinion/2015/06/30/hail-the-humble-paddy, 2021. [Online; accessed 5-July-2021]. ↩
B. M. S. Basnet. Rice and food security: Serious constraints. url: https://thehimalayantimes.com/opinion/rice-food-security-serious-constraints/, 2021. [Online; accessed 5-July-2021]. ↩
Nalley. Economic and environmental impact of rice blast pathogen alleviation in the united states. PLoS ONE, 2016. ↩
Ricepedia. The Global Staple. url: https://ricepedia.org/rice-as-food/the-global-staple-rice-consumers, 2020. [Online; accessed 5-July-2021]. ↩